Victor De Schwanberg/Science Photograph Library by way of Getty Pictures
Regardless of greater than a decade of reminding, prodding, and downright nagging, a stunning variety of builders nonetheless can’t convey themselves to maintain their code freed from credentials that present the keys to their kingdoms to anybody who takes the time to search for them.
The lapse stems from immature coding practices wherein builders embed cryptographic keys, safety tokens, passwords, and different types of credentials instantly into the supply code they write. The credentials make it simple for the underlying program to entry databases or cloud providers crucial for it to work as meant. I printed one such PSA in 2013 after discovering easy searches that turned up dozens of accounts that appeared to expose credentials securing computer-to-server SSH accounts. One of many credentials appeared to grant entry to an account on Chromium.org, the repository that shops the supply code for Google’s open supply browser.
In 2015, Uber discovered the laborious method simply how damaging the follow could be. A number of builders for the journey service had embedded a singular safety key into code after which shared that code on a public GitHub web page. Hackers then copied the important thing and used it to entry an inside Uber database and, from there, steal sensitive data belonging to 50,000 Uber drivers.
Uber attorneys argued on the time that “the contents of those inside database recordsdata are carefully guarded by Uber,” however that competition is undermined by means the corporate took in safeguarding the info, which was no higher than stashing a home key beneath a door mat.
The variety of research printed since following the revelations underscored simply how widespread the follow had been and remained within the years instantly following Uber’s cautionary story. Sadly, the negligence continues even now.
Researchers from safety agency GitGuardian this week reported discovering nearly 4,000 distinctive secrets and techniques stashed inside a complete of 450,000 initiatives submitted to PyPI, the official code repository for the Python programming language. Practically 3,000 initiatives contained not less than one distinctive secret. Many secrets and techniques have been leaked greater than as soon as, bringing the full variety of uncovered secrets and techniques to nearly 57,000.
“Exposing secrets and techniques in open-source packages carries important dangers for builders and customers alike,” GitGuardian researchers wrote. “Attackers can exploit this info to achieve unauthorized entry, impersonate bundle maintainers, or manipulate customers by way of social engineering techniques.”
The credentials uncovered offered entry to a spread of assets, together with Microsoft Energetic Listing servers that provision and handle accounts in enterprise networks, OAuth servers permitting single sign-on, SSH servers, and third-party providers for buyer communications and cryptocurrencies. Examples included:
- Azure Energetic Listing API Keys
- GitHub OAuth App Keys
- Database credentials for suppliers similar to MongoDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL
- Dropbox Key
- Auth0 Keys
- SSH Credentials
- Coinbase Credentials
- Twilio Grasp Credentials.
Additionally included within the haul have been API keys for interacting with varied Google Cloud providers, database credentials, and tokens controlling Telegram bots, which automate processes on the messenger service. This week’s report mentioned that exposures in all three classes have steadily elevated prior to now 12 months or two.
The secrets and techniques have been uncovered in varied sorts of recordsdata printed to PyPI. They included major .py recordsdata, README recordsdata, and check folders.
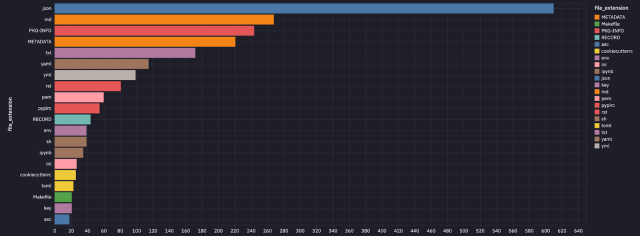
GitGuardian
GitGuardian examined the uncovered credentials and located that just about 768 remained energetic. The chance, nevertheless, can prolong nicely past that smaller quantity. GitGuardian defined:
It is very important observe that simply because a credential can’t be validated doesn’t imply it needs to be thought-about invalid. Solely as soon as a secret has been correctly rotated can you recognize whether it is invalid. Some sorts of secrets and techniques GitGuardian continues to be working towards robotically validating embody Hashicorp Vault Tokens, Splunk Authentication Tokens, Kubernetes Cluster Credentials, and Okta Tokens.
There are not any good causes to show credentials in code. The report mentioned the most typical trigger is by chance.
“In the midst of outreach for this mission, we found not less than 15 incidents the place the writer was unaware they’d made their mission public,” the authors wrote. “With out naming any names, we did wish to point out a few of these have been from very massive corporations which have sturdy safety groups. Accidents can occur to anybody.”
Over the previous decade, varied mechanisms have develop into out there for permitting code to securely entry databases and cloud assets. One is .env recordsdata which are saved in non-public environments outdoors of the publicly out there code repository. Others are instruments such because the AWS Secrets and techniques Supervisor, Google Cloud’s Secret Supervisor, or the Azure Key Vault. Builders may make use of scanners that examine code for credentials inadvertently included.
The examine examined PyPI, which is only one of many open supply repositories. In years previous, code hosted in different repositories similar to NPM and RubyGems has additionally been rife with credential publicity, and there’s no motive to suspect the follow doesn’t proceed in them now.








